Describe Chromatin and How It Changes
The primary functions of chromatin are. The structural strength offered by chromatin prevents DNA damage during cell division.
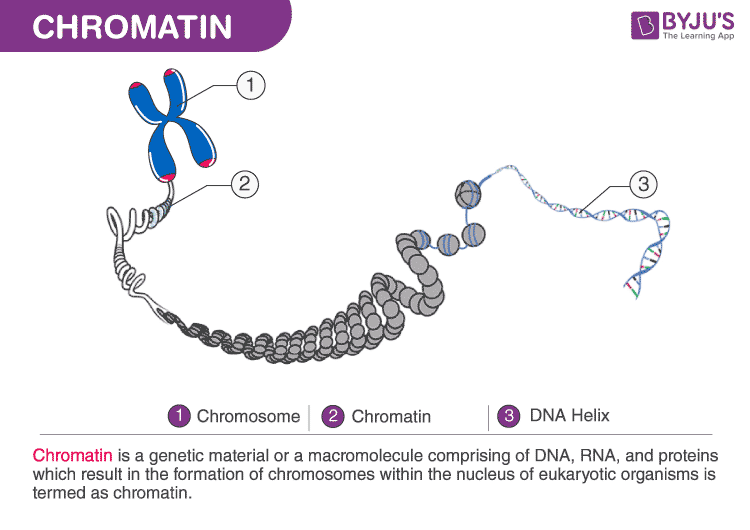
Chromatin Structure Functions And Chromatin Analysis
The major proteins in chromatin are histones which help package the DNA in a compact form that fits in the cell nucleus.

. Chromatin packaging is important in that the chromatin must be condensed into the X shaped chromosomes to be able to be split correctly in anaphase. Thus the morphology of chromatin changes to allow access to genetic information and assist other functions. Modifications on histones assist in the recognition and accessibility of sites where DNA repair needs to take place.
Chromosomal structure is not inert. Chromatin generates a barrier for the repair of DNA damage. The histone proteins organize the DNA into special structures called nucleosomes.
Its prime function is packaging very long DNA molecules into a denser shape compact which stops the strands from becoming tangled and plays vital roles in strengthening the DNA during cell division avoiding DNA damage and controlling gene expression and DNA replication. Chromatin is a substance within a chromosome consisting of DNA and protein. It is composed of DNA and proteins that condense to form chromosomes.
Chromatin is only an exceptional of DNA and fats that generates chromosomes contained inside the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells. Aging is Associated with Changes in Chromatin. Alterations to the chromatin structure occur as a consequence of the limitations acquired through its condensation.
Arrow_forward How is chromatin immunoprecipitation used to determine the locations of histone modifications in the genome. Chromatin is the combination of DNA and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell. Briefly describe three ways that ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes may change chromatin structure.
Chromatin is always present in the nucleus of our cells. Opens up the DNA allowing assembly of general transcription aparatus. Chromatin is labeled with the vital fluorophore Hoechst 33342.
To package DNA into a smaller volume to fit in the cell to strengthen the DNA to allow mitosis and meiosis and prevent DNA damage and to control gene expression and DNA replication. Activity and considering that the aging process is genetically driven. Chromatin The complexes between eukaryotic DNA and proteins are called chromatin which typically contains about twice as much protein as DNA.
Chromatin is a complex of RNA DNA and protein can be seen in eukaryotic cells. The DNA carries the cells genetic instructions. A substance within a chromosome consisting of DNA and protein nucleosome.
The nucleosome further folds to form a chromatin fibre. Genome-wide contact patterns of chromosome at high precision uncover fine structural properties conductive to exploring underlying mechanisms on structure establishment and function realization for chromatin. Euchromatin has a less compact structure and is often described as a 11 nm fiber that has the appearance of beads on a string where the beads represent nucleosomes and the string represents DNA.
Recent progress has defined the molecular machines and events that. Yet none the less it is in fact exceptionally pliable and wrapped round nuclear fats also as an easy system to asses through the nucleus. Our conditions of dye concentration and irradiation allow a continuous following of the dynamics of changes without major perturbation.
Describe how chromatin is packaged in a eukaryotic chromosome. Histone proteins are the basic packers and arrangers of chromatin and can be modified by various post-translational modifications to alter chromatin packing histone modificationMost modifications occur on histone tails. Its primary role is to package DNA into structures known as nucleosomes and wrap them around a base.
Post-translational modifications and biochemical remodelling of chromatin. Chromatin is located in the nucleus of our cell. Chromatin remodeling is an integral aspect of epigenetic changes in the body which is the result of modifications to gene expression rather than modification of genetic sequences themselves.
The consequences in terms of chromatin accessibility and compaction depend. Chromatin helps with the compaction of the DNA inside a cell. Chromatin is the most complex among self-reproducible parts of the cell.
Changes in chromatin structure are associated with DNA replication and gene expression. The major proteins of chromatin are the histones small proteins containing a high proportion of basic amino acids arginine and lysine that facilitate binding to the negatively charged DNA molecule. This phosphorylation extends over.
Current research has also revealed that chromatin plays an important role in signaling DNA damage and assisting in its repair. Traditionally interphase chromatin is classified as either euchromatin or heterochromatin depending on its level of compaction. Atomic DNA would not seem to be in free of charge linear strands.
It compresses the DNA structure into a compact unit so that it can fit within the nucleus. Chromatin undergoes various structural changes during a cell cycle. Thats why its symmetrical.
Physically bind and push the histones out of the way using energy. What is Chromatin. Large ATP-dependent complexes that temporarily change nucleosomal structure so DNA becomes less tightly bound to histone core.
A section of DNA that is wrapped around a core of proteins RNA polymerase. A very sophisticated structure of chromatin makes possible the differential transcription of a genetic programme which supports the accurate specialized functions of each cell in interphase and also provides a mechanism for perfect reproduction of this complex machinery of genetic information during. Studies of the molecular mechanisms regulating the condensation and decondensation of chromosomes during the cell cycle demonstrate that gross morphological changes in chromatin structure are driven through reversible modification of chromosomal proteins.
One of the earliest recognized responses to DNA damage is the phosphorylation of the histone variant γ-H2AX in mammalian cells Fillingham et al 2006. It starts to condense in prophase the chromosomes go to the center in metaphase split in anaphase decondenses in telophase. As chromatin is condensed into the primary nucleosome structure DNA becomes less accessible for transcription factors.
Since chromatin structure is responsible for modulation of gene. There are certain changes that occur in chromatin due to gene expression and DNA replication. We combine these observations with ultrastructural analysis performed by electron microscopy of the same eggs fixed at chosen stages.
In this short review we describe changes of chromatin structure during various biological processes from a DNA sequence view with an increase of. These can also re-form the nucleosomes when transcription is finished.

Chromatin Structure Dna Is Wrapped Around A Histone Octamer To Form Download Scientific Diagram
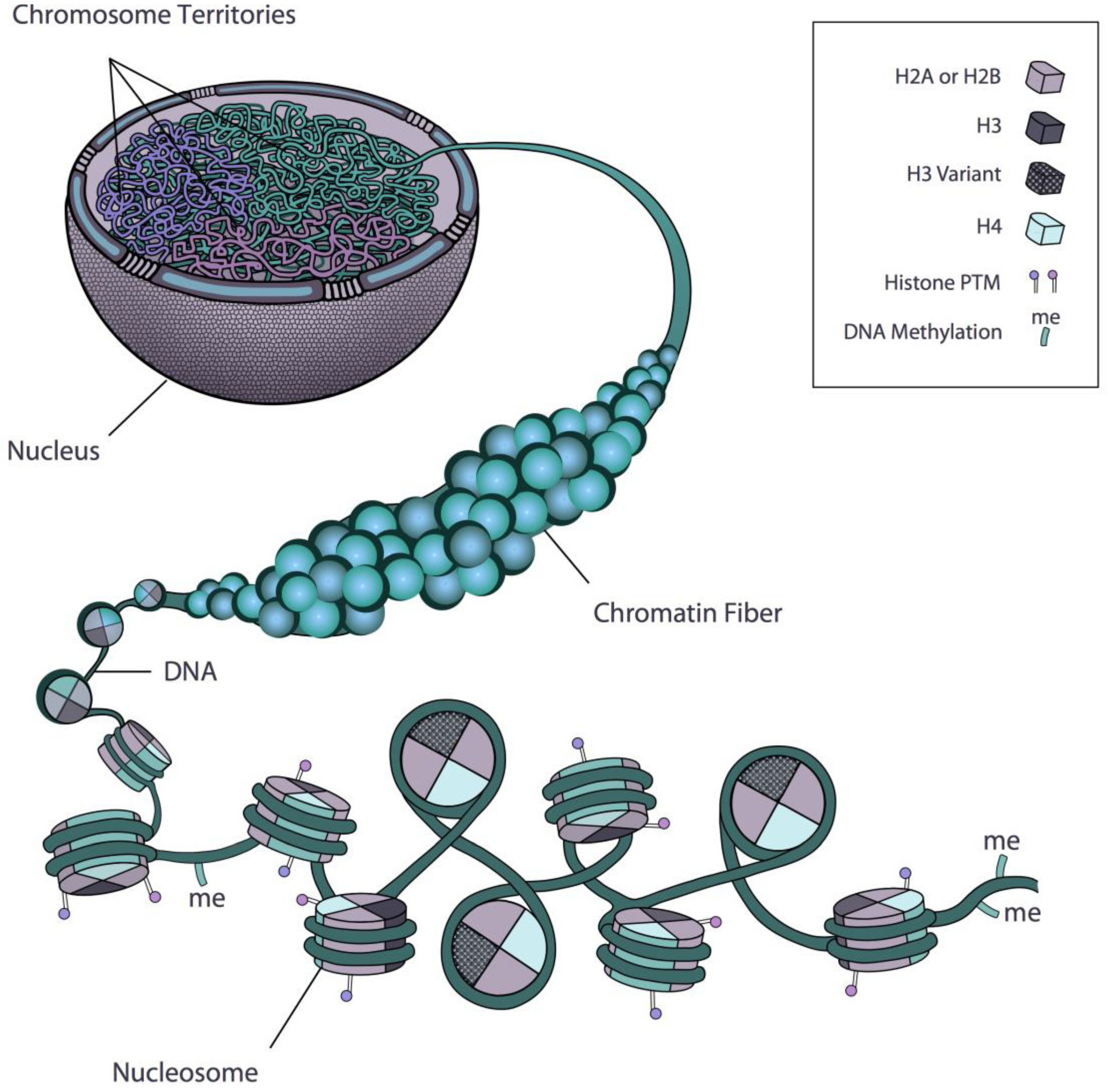
Biology Free Full Text Insights Into Chromatin Structure And Dynamics In Plants Html
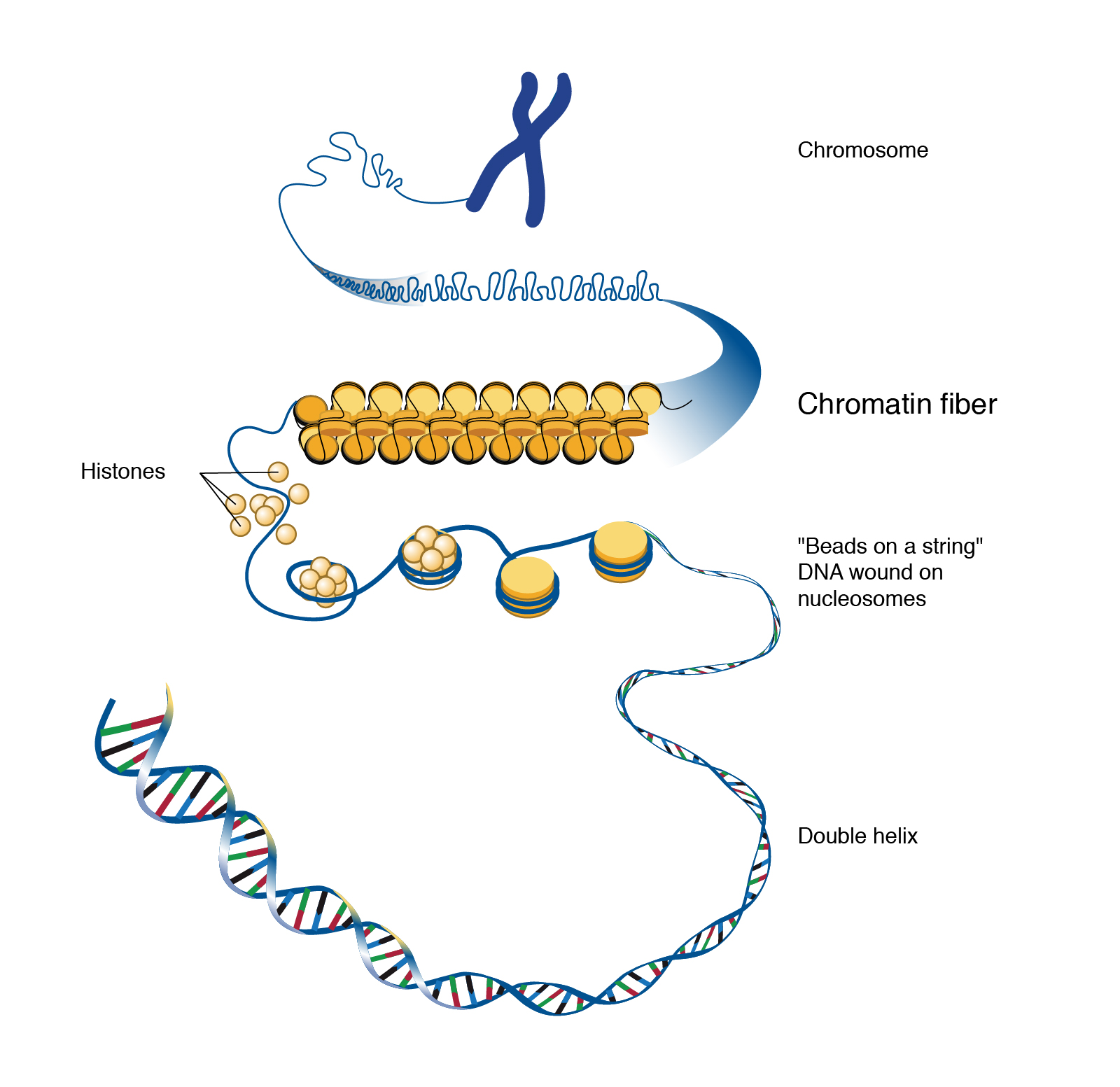
No comments for "Describe Chromatin and How It Changes"
Post a Comment